In my previous article, I introduced you to the world of Web3 and blockchain, touching on how this technology works behind the scenes. Today, let’s dive deeper into the “magic trick” that makes blockchain trustworthy without needing a boss or central authority.
Imagine Blockchain as a Giant Village Ledger
Picture this: there’s a huge notebook placed right in the middle of a village square. Everyone in the village can come and write on it. Once you write something, it stays there forever – nobody can erase it or secretly edit it later.
Every page in this notebook is called a block. When these pages are connected chronologically, they form a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain.
Now, imagine you want to record that you gave your friend 1 Bitcoin for a delicious pizza. The question is: who gets to write this transaction on the next page of the notebook? And how do we make sure they write the truth and not something fake?
That’s where two key mechanisms come in: Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). Let’s explore them through everyday analogies.
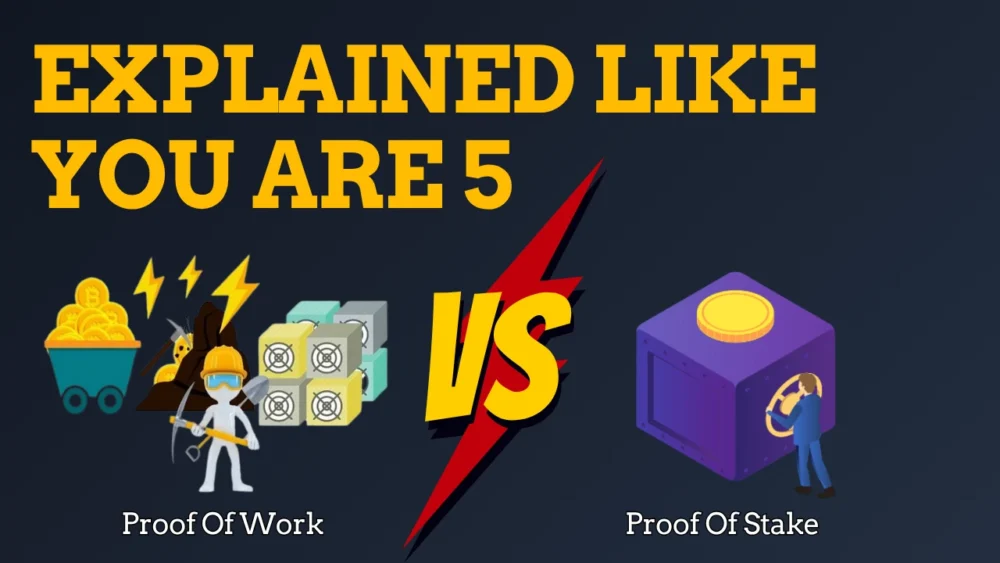
Proof of Work (PoW): The Great Puzzle Contest

Bitcoin uses this method. Everybody called this method as “mining”.
Think of PoW as a puzzle race.
Imagine every time the villagers need to add a page to the notebook, they hold a contest:
Who can solve this extremely difficult math puzzle first?
It’s like trying to guess the correct combination of a giant lock with trillions of possible numbers. Everyone (the miners) starts guessing at the same time.
Once someone finally solves it, they announce the answer loudly to the village. Everyone checks it quickly (since verification is easy once you know the answer). The winner then gets to write the next page in the notebook and receives a reward: newly minted Bitcoin plus transaction fees.
Here’s a simple analogy:
Think of a classroom where the teacher says: “Whoever solves this super hard sudoku puzzle first will get a chocolate.”
All students rush to solve it. The fastest one gets the chocolate. But all the others still used their energy for nothing.
That’s why PoW uses huge amounts of electricity. All miners compete using high-powered computers that consume energy non-stop, just to earn the chance to add the next block.
Proof of Stake (PoS): The Lottery of Trust

Ethereum used to use PoW but switched to PoS in 2022 to save energy and become eco-friendly.
Here’s how PoS works:
Instead of running energy-hungry puzzles, villagers stake (lock up) some of their coins as a security deposit. It’s like placing collateral to show you’re serious.
Imagine:
Each villager puts some of their coins into a bowl. The more coins you put in, the higher your chance of being chosen.
Then, a villager is randomly picked (weighted by their stake) to write the next page in the notebook and earn a reward. It’s like a lottery system, but fairer, because:
- You keep your coins as long as you act honestly.
- If you try to cheat, your staked coins can be slashed (burned as punishment).
This method uses far less energy than PoW, yet still secures the network effectively.
Why Do We Even Need These Systems?
Both PoW and PoS are designed to solve a classic dilemma called the Byzantine Generals Problem. Sounds complicated, but here’s the gist:
How can multiple people, who don’t fully trust each other, agree on a single truth without needing a boss?
In blockchain:
- PoW uses computational effort as proof of honesty.
- PoS uses economic stake as proof of honesty.
Both ensure that everyone plays fair, or risks losing their resources.
Which Is Better?
- PoW (like Bitcoin) is ultra-secure but consumes massive energy, almost like factories running 24/7 to solve endless sudoku puzzles.
- PoS (like Ethereum now) is energy-efficient and scalable but can risk giving more influence to those with bigger stakes, like buying more lottery tickets increases your chance of winning.
Both have their strengths and weaknesses, and developers continue exploring newer models like Delegated PoS or hybrid systems to find the sweet spot between decentralization, security, and efficiency.
Trust Without a Boss
Next time someone dismisses blockchain as mere hype, you can explain:
It’s a public notebook that uses either puzzle competitions (PoW) or economic lotteries (PoS) to ensure everyone agrees on what’s true.
It’s not just about crypto coins. Blockchain is a new foundation for recording and verifying truth without relying on a central authority. In a world where trust is expensive, blockchain creates trustless trust – a concept that may shape the future of digital interactions, finance, and beyond.
What’s your take on this? Share your thoughts in the comments – I’d love to hear your perspective.
If there’s something you want me to cover next, just let me know. You can follow me here on my Medium to get my latest updates as soon as they drop! You can also contact me through X @AskaraJr and Linkedin